How Big is a Bed Bug



The stealthiest of all sea creatures, the Octopus does not rely on its tentacles alone. Taking advantage of its innate camouflage techniques and its various sizes, it remains ever elusive.
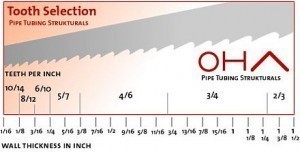
Saws come in various sizes and shapes. Discover the different saw sizes and how each one can differ from the other. Gather information about saws and use the tool in the most efficient way possible.
The pomfret refers to several types of fish set under the Bramidae family. The size of the pomfret varies among species, with many over 3 ft long. There are many species known as pomfret, including some from other fish families.

The biggest ants in the world best exemplify the term “small but terrible.” But the largest members of each species can be described as literally “queen-sized.”

The T-rex specifically refers to the Theropod dinosaur species called Tyrannosaurus rex. It was considered an apex predator, which preyed on ceratopsians and hadrosaurs. Aside from these details, there are other interesting facts to learn about it including the different T-rex sizes.

Dresses are available in different styles, but the sizes used are now standardized. There are sized for women, petite, junior and many others. Before you buy a dress, being aware of these standard dress sizes will be absolutely necessary.