Dimension of a Medical Ventilator
The medical ventilator refers to any device that is used to help a 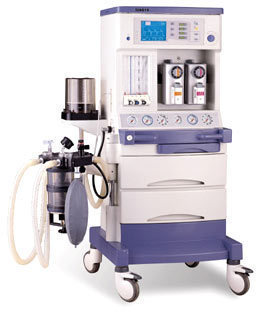 person breathe. Also known as mechanical ventilators, these are frequently utilized during surgery when the patient is asleep.
person breathe. Also known as mechanical ventilators, these are frequently utilized during surgery when the patient is asleep.
Medical Ventilator Dimensions
The specifications here are for the Newport HT70 ventilator. The following do not necessarily apply to other ventilators, but they can form the basis for comparison.
The patient range is infant/pediatric (≥5 kg) – adult. The VT or tidal volume is 50 to 2,200 ml. The respiratory rate is 1 to 99 b /min and the inspiratory time is 0.1 to 3.0 sec. The pressure support is 0 to 60 cmH 2 O/0 to 60 mbar and the PEEP/CPAP is 0 to 30 cmH 2 O/0 up to 30 mbar.
The flow is 6 to 100 L/min and the pressure control is 5 to 60 cmH 2 O/5 to 60 mbar. The I:E ratio is 1:99 to 3:1. The Ptrig (sensitivity) is -9.9 to 0 cmH 2 O/-9.9 and up to 0 mbar.
The manual inflation is 3 seconds maximum and the bias flow is 7 L/min with PEEP and 3 to 30 L/min if the NIV is on. The PS max time is 0.1 to 3.0 seconds.
How does the Ventilators Work?
Regardless of the differences in medical ventilator dimensions, their role is basically the same. They will inject air and oxygen into the lungs. The ventilator improves the patient’s oxygen level.
The ventilator also takes out the carbon dioxide that makes it hard for the patient to breathe. If necessary, the ventilator will give complete support. This means the machine will help the patient breathe some more.
Before an individual can be set on the ventilator, a breathing tube will be placed in the airway. This is placed in the patient’s mouth. If the situation calls for a tracheotomy, it will be performed instead. After the trachea incision, the tracheotomy tube will be set. This process is often preferred if long term use of the ventilator is required.
The ventilator can also be set to various modes depending on the support required. As indicated in the specifications given earlier, the respiratory rate and other elements can be modified and precisely set.
It isn’t just the medical ventilator dimensions that vary, but also the features of the machines. The ventilators used in hospitals are complex with numerous control settings. The parameters of these devices are also quite extensive and diverse.